Three Activist Movements that have hit the Corporate World
Focus on these disruptions that first started in the United States
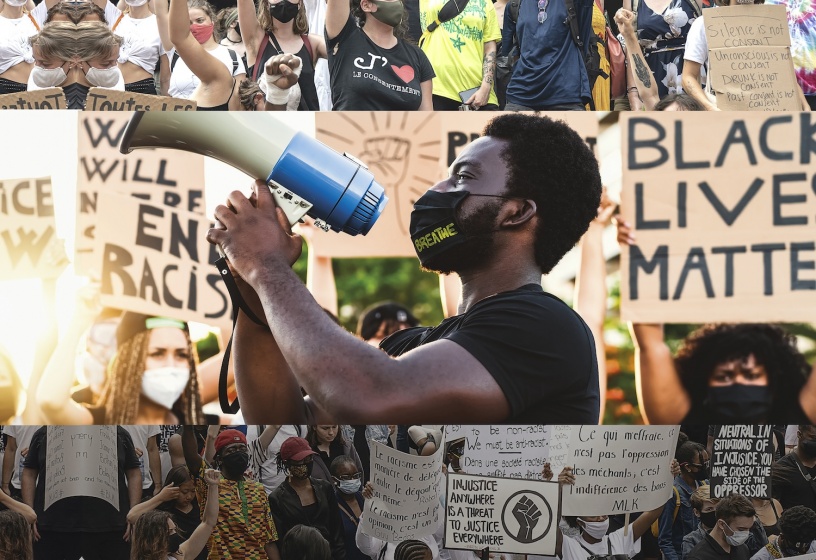
Black Lives Matter
The Black Lives Matter (BLM) movement began in 2013, following the acquittal of George Zimmerman in the fatal shooting of Trayvon Martin, an unarmed Black teenager. Alicia Garza, Patrisse Cullors, and Opal Tometi, three Black women activists, founded the movement in response to what they saw as a pattern of systemic racism and police brutality against Black people in the United States.
The movement gained wider attention in 2014, following the deaths of Michael Brown in Ferguson, Missouri, and Eric Garner in New York City, both at the hands of police officers. These deaths sparked protests across the country, with activists using the hashtag #BlackLivesMatter to draw attention to issues of police brutality and systemic racism.
The Black Lives Matter movement has significantly impacted the workplace, with many companies recognising the need to address such issues. This has led to an increased focus on diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives. Many companies are making public commitments to improve the representation of racialised people in leadership positions and in the workforce more broadly. The movement has prompted companies to examine their policies and practices for potential biases or disparities and take concrete steps to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion. Examples of this impact include companies declaring June 10th a holiday and making public statements condemning racism and police brutality, as well as donations to organisations supporting racial justice and equality.
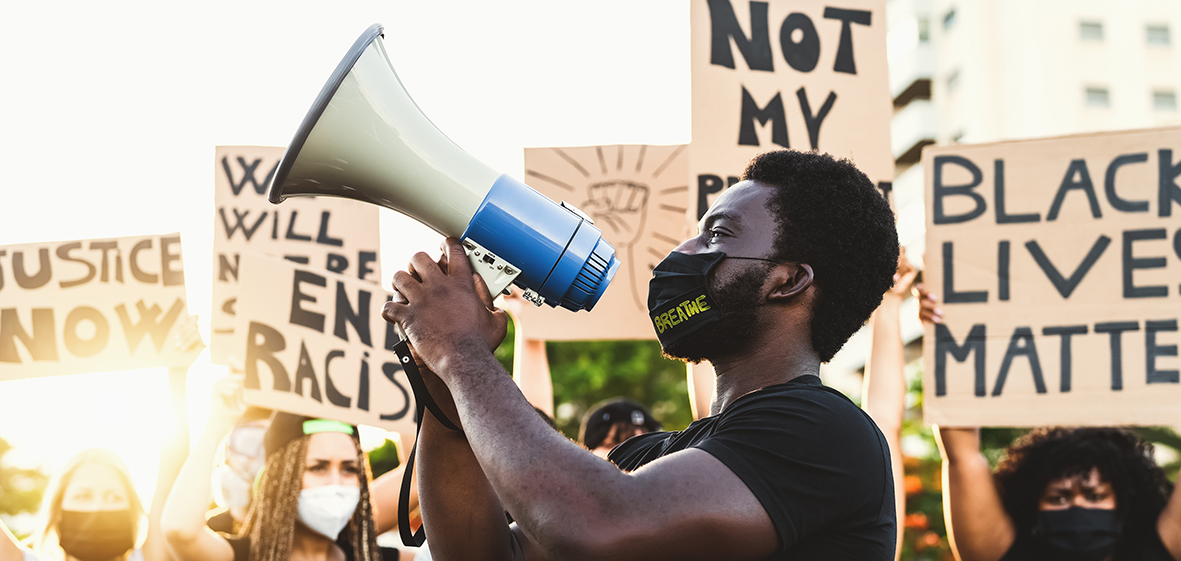
#MeToo movement
The #MeToo movement accelerated in 2017 as a response to the widespread sexual harassment and assault allegations against Hollywood producer Harvey Weinstein. The phrase Me Too was actually originally coined by Tarana Burke, an African-American civil rights activist, as a way to raise awareness of sexual assault and harassment, particularly among women of colour. However, the movement gained significant momentum after the allegations against Weinstein were made public. Women and men across various industries and countries began sharing their stories of sexual harassment and assault on social media using the hashtag #MeToo. The movement quickly went viral, with millions worldwide sharing their experiences and calling for greater awareness and action to address sexual harassment and assault.
The #MeToo movement has had a significant impact on the workplace, particularly in terms of raising awareness of sexual harassment and assault, promoting gender equality, and encouraging employers to adopt more inclusive policies and practices. For in many cases, sexual harassment and assault can be seen as symptoms of wider gender inequalities in the workplace, such as pay gaps and lack of representation in leadership positions. The movement has helped to create a more supportive and safer workplace environment for women and has forced many employers to confront and address issues of power dynamics and gender inequality in the workplace.
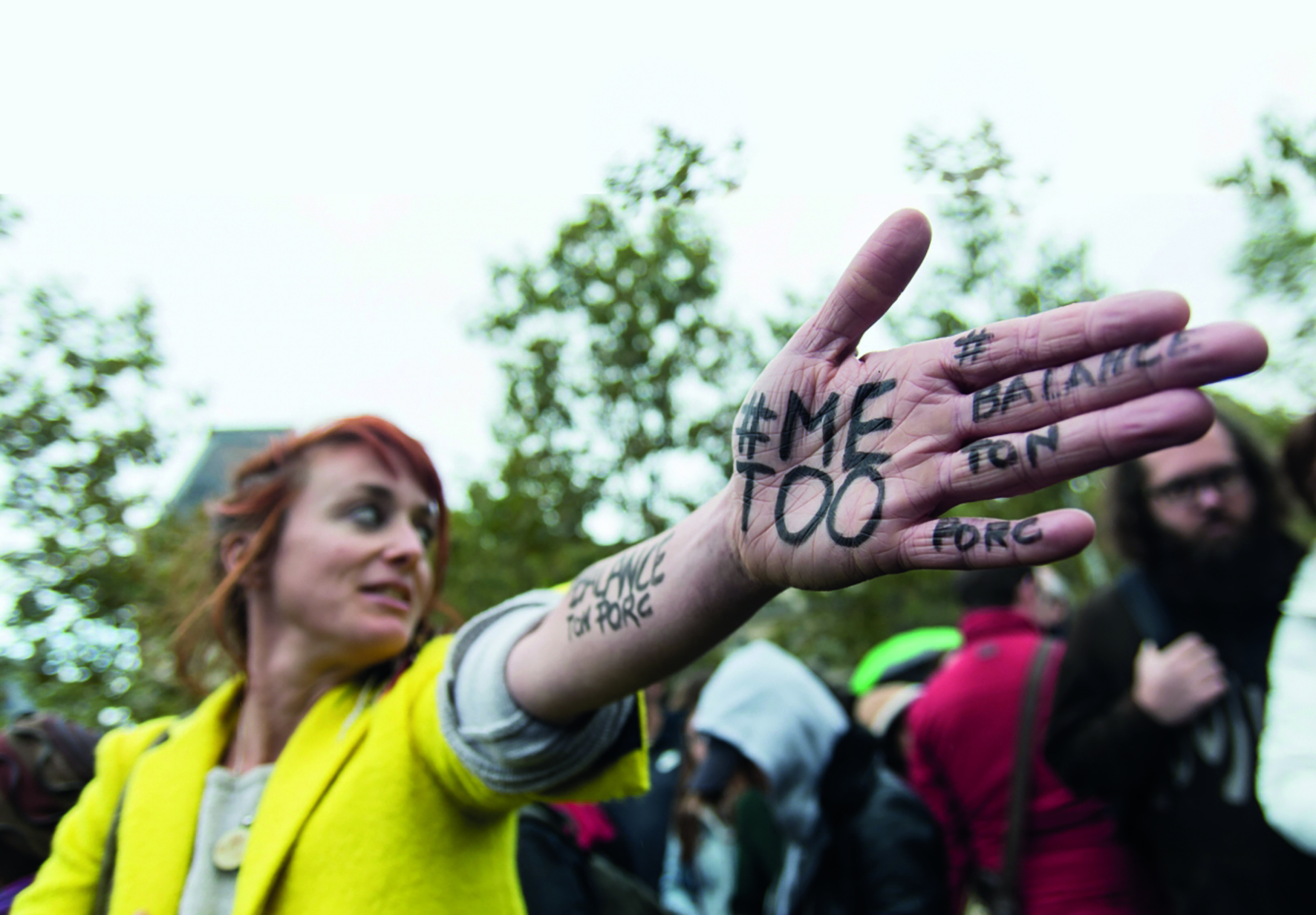
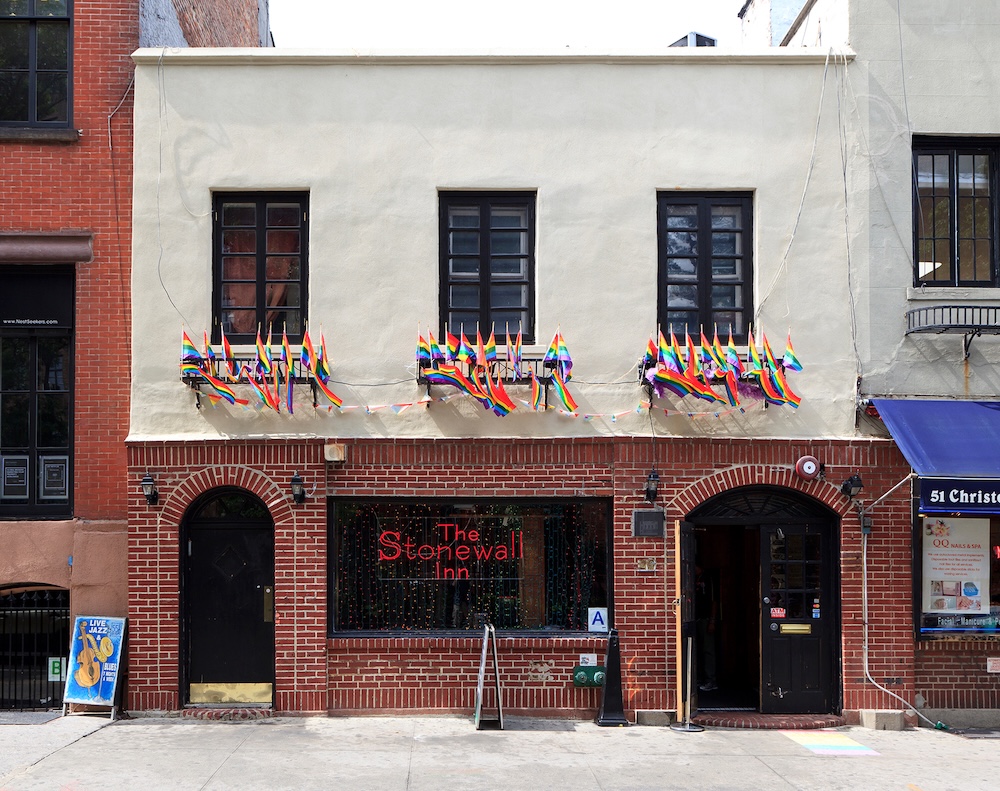
Stonewall Uprisings
The Stonewall uprising was a series of protests and demonstrations that took place in June 1969 in New York City, specifically at the Stonewall Inn, a popular gay bar in the Greenwich Village neighborhood. On the night of June 28, 1969, police raided the Stonewall Inn, as they frequently did with gay bars at the time. However, on this particular night, patrons of the Stonewall Inn refused to comply with the police, and an uprising broke out. The protest lasted for several days and sparked a broader movement for LGBTIQ+ rights and liberation.
More than 50 years after, other LGBTIQ+ social movements, such as ACT UP and the marriage equality movement, or more recently the rainbow armbands case during the football world cup in Qatar, participated in raising awareness of these issues. In terms of specific examples, the impact of LGBTIQ+ social movements on the workplace can be seen in some high-profile cases. For example, in 2019, a group of more than 200 companies signed an amicus brief supporting transgender rights in a Supreme Court case involving transgender discrimination in the workplace.
LGBTIQ+ social movements have significantly impacted the workplace, particularly in terms of promoting greater inclusion and diversity, advocating for legal protections and rights for LGBTIQ+ employees, and pushing for greater corporate social responsibility and ethical business practices. The movement has helped to create a more supportive and welcoming workplace environment for LGBTIQ+ employees and has forced many employers to confront and address issues of discrimination and harassment based on sexual orientation or gender identity.

Also to read in the dossier« When Diversity Activism Shakes the Workplace »:
