AI : Innovations For Good

Health, biodiversity, climate… Artificial intelligence is advancing rapidly to tackle the challenges of our time. When properly directed, this technology reveals its full potential. Here’s a selection of promising innovations.
AI-driven Climate Insurance
Over 62% of global climate-related risks remain uninsured. IBISA, a dynamic start-up based in Luxembourg, fills this gap with innovative solutions. The start-up relies on 'parametric' insurance: a model based on a set of predefined climatic indicators, rather than on 'post-incident' assessments. By using satellite data combined with artificial intelligence, IBISA analyses climatic events over the past 30 years in specific geographic regions. This approach enables the development of insurance products tailored particularly for farmers and the energy sector. Today, this innovative model has already protected over 500,000 farms in high climate-risk regions.

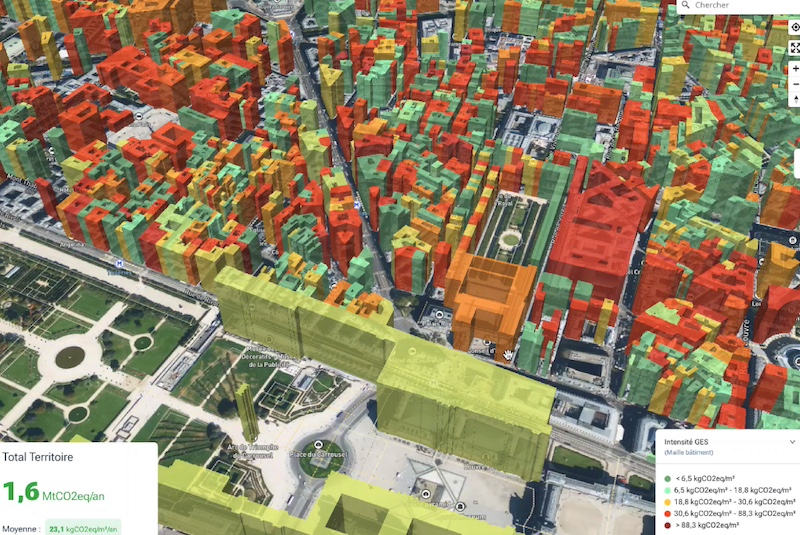
Real-time Mapping to Decarbonise Cities
Nexqt, an urban decarbonisation platform, aims to address the urgent need for cities, which account for 70% of global CO2 emissions, to implement concrete climate solutions. The start-up relies on a technology to analyse real-time data on urban emissions, including those from buildings or transportation, thus enabling various stakeholders to identify priority areas for action. The platform is not only limited to large cities: it is designed to be used by any locality. In fact, several municipalities in Luxembourg, have already embraced the tool without hesitation.
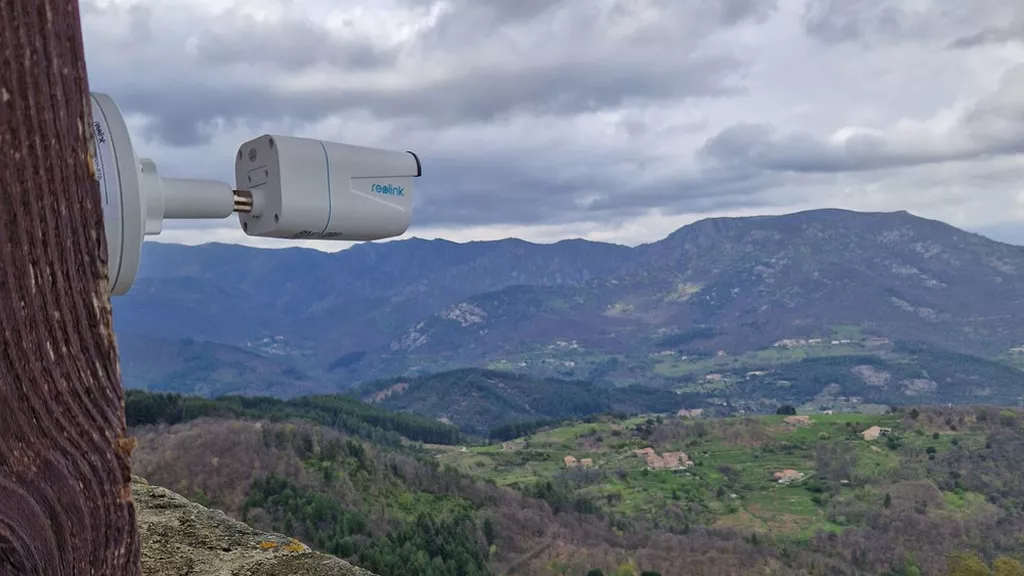
Forest Fire Alert!
Pyro-Station, a collaboration between Pyronear and Data For Good, is a tool designed to quickly detect forest fire outbreaks when they are still just smoke. Equipped with smart cameras installed on old firefighter lookout towers, the technology continuously monitors forested areas, sending immediate alerts to fire stations as soon as the first distinctive signs of a fire appear. By intervening very early, rescue teams increase their chances of containing the fire by more than 90%, according to Théo Alves da Costa, co-president of Data For Good. Deployed in both France and Chile, this initiative is fully open source and aims to protect our forests effectively.

The Pharma and Biotech GPT
Founded in 2023 in Luxembourg, Helical stands out for its commitment to democratising artificial intelligence in the field of biology, by developing models based on DNA and RNA. These innovative tools allow scientists to simulate experiments, for example, by conducting tests on a virtual cell, enabling them to test new treatments more quickly and accurately. This approach also reduces the reliance on animal and human testing. This technology transform agricultural sciences, enabling the production of crops more resistant to various climate constraints. The Helical platform is open source, ensuring these advances are made available to all researchers.

AI Helping Refugees
The UNHCR (United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees), supporting more than 120 million displaced people worldwide, also uses artificial intelligence in various ways to improve humanitarian conditions. For instance, AI is being used to develop a global early warning system to anticipate forced displacement and help to better prepare humanitarian interventions. Another initiative, Hatefree, analyses a range of data related to online hate speech to counter xenophobia targeting refugees. Finally, AI is also used by the UNHCR to promote the financial inclusion of refugees by providing them access to banking services. As Hovig Etyemezian, Head of Innovation, explains "the ultimate goal is to solve real problems that real people are facing".
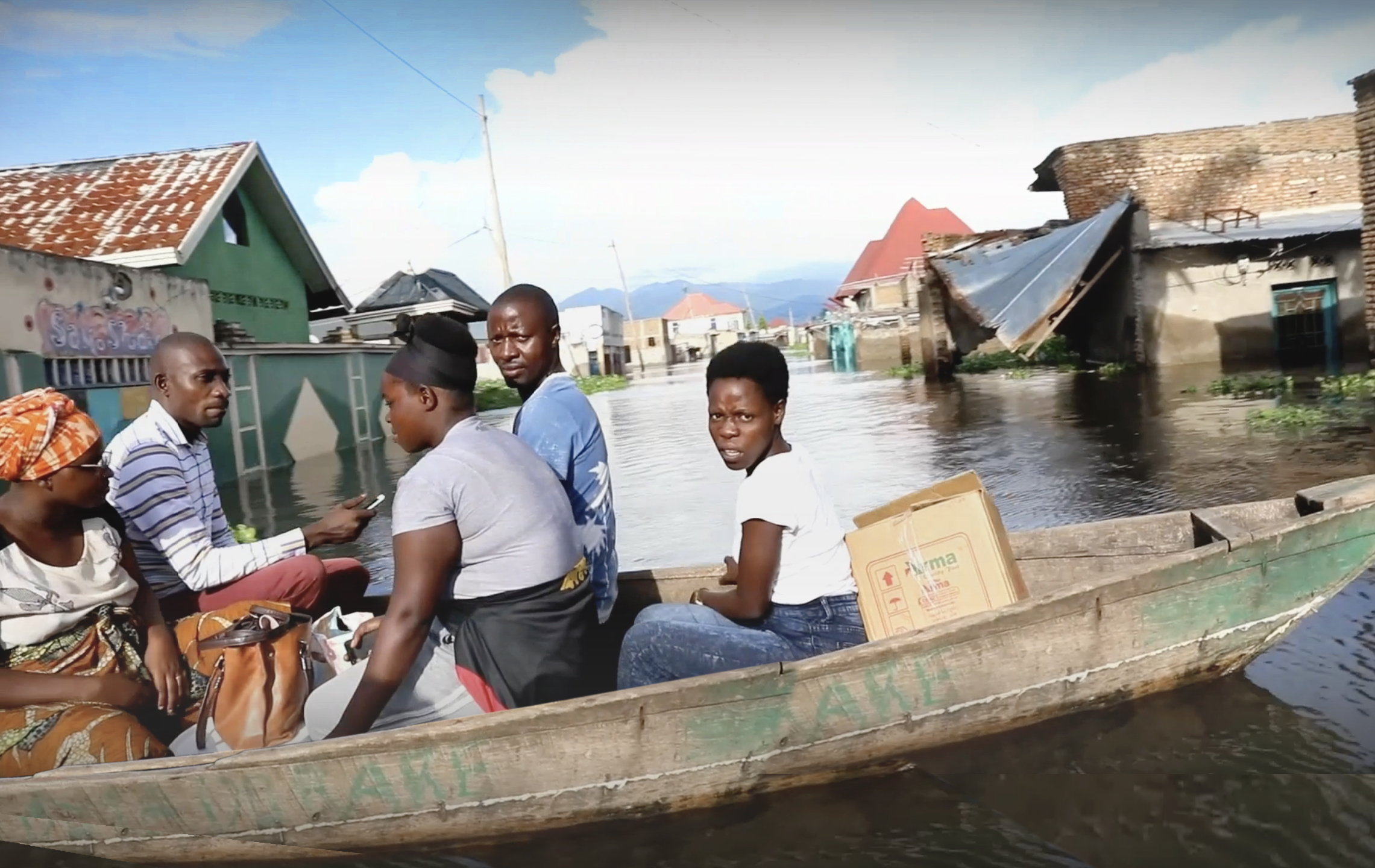

Protecting Biodiversity
Space4good uses satellite imagery and technologies such as laser scanning,
to process massive volumes of data in order to monitor, model, and protect ecosystems. This is how AI can contribute to preserve biodiversity. One such project, based in Amsterdam, has classified trees by species and health status, while in Indonesia, dense forests have been mapped to identify valuable trees, even in areas inaccessible to humans. Combining AI with acoustic sensors, also enables the detection of animal species based on the sounds they produce, thus contributing to more efficient and sustainable ecosystem management.

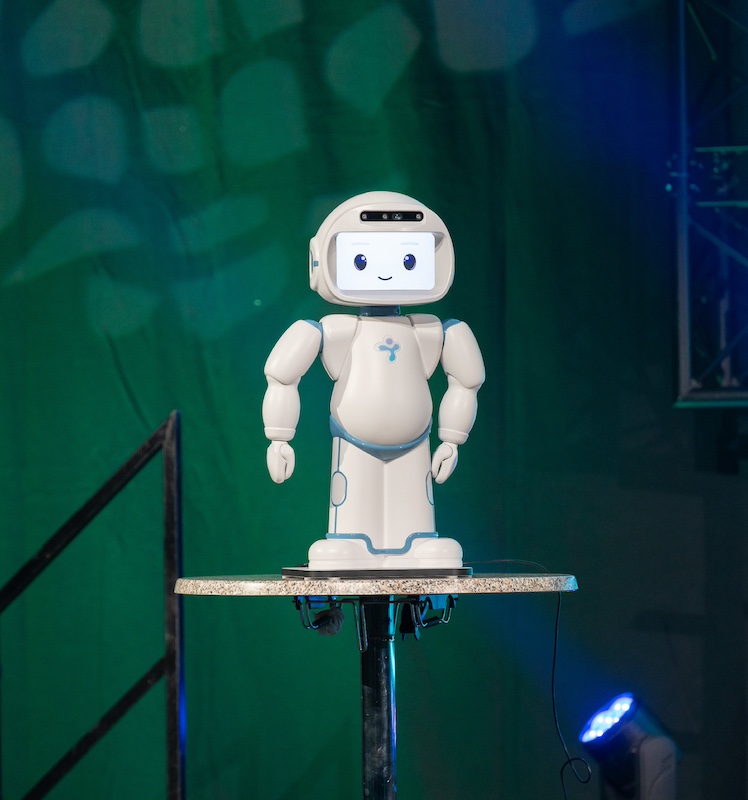
A Humanoid Robot for Specific Educational Needs
The robot, created by LuxAI, incorporates artificial intelligence to support children with specific educational needs, particularly those with autism. The 'QTrobot' is designed to address long waiting times for care by offering a playful and interactive approach, tailored to each child. It also serves as a platform for research on human-robot interactions and has the potential to benefit other groups as well, such as people with dementia or those experiencing loneliness.

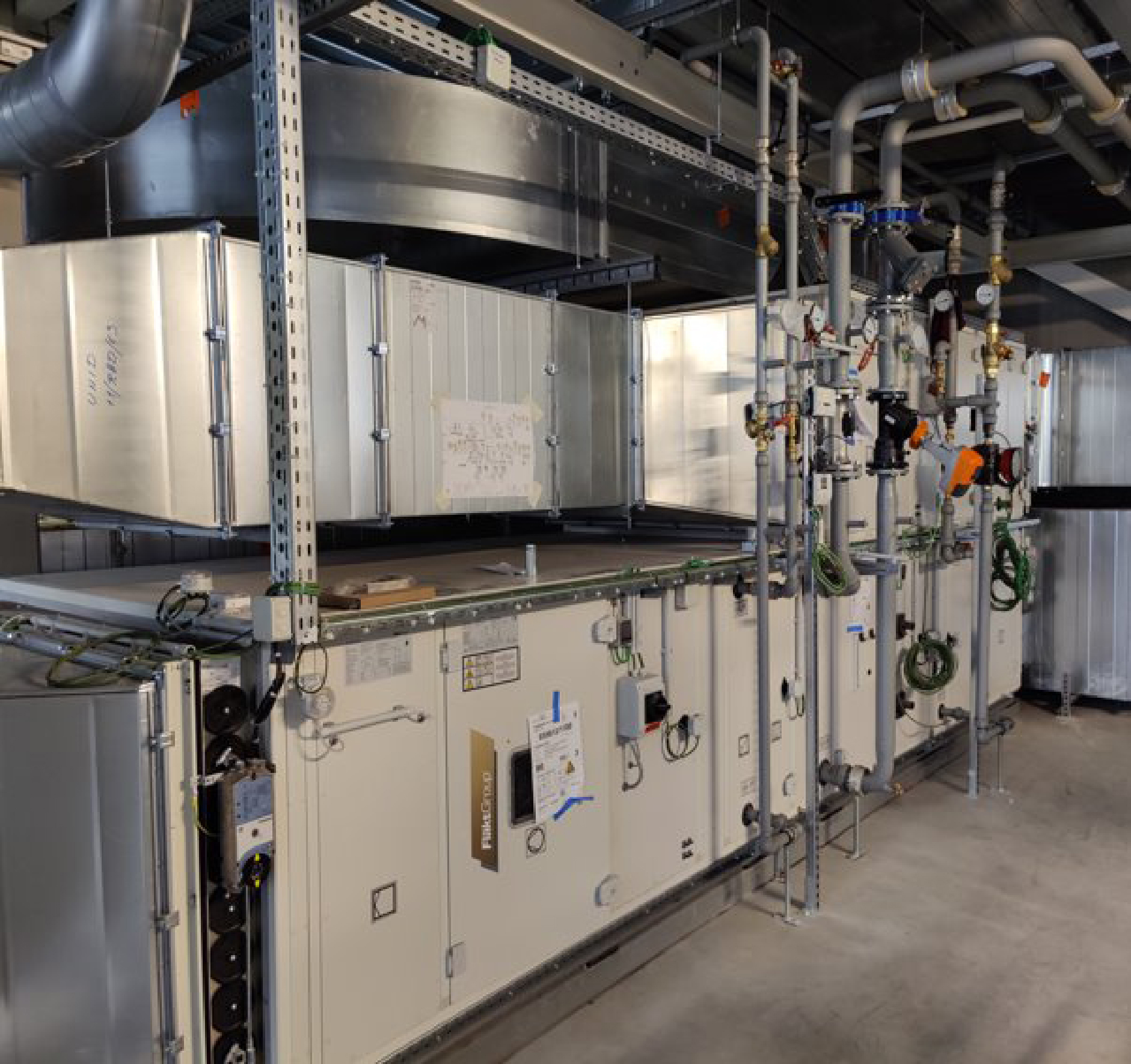
Cutting Industrial Emissions
The industrial sector is responsible for 29% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with air treatment in the pharmaceutical industry accounting for as much as 40% of the total energy consumption of facilities. This is one of the key challenges that Pepite aims to address through artificial intelligence. By applying machine learning algorithms with limited energy consumption, the Belgian company optimises air treatment units. The result is a 27% reduction in energy consumption for these units, saving gigawatt-hours of electricity and cutting the emission of thousands of tons of CO2 each year.

Also to read in the dossier ''AI, Encouraging Techno-Awareness'':



